Wash Water
Backwash water generated in drinking and process water treatment is effectively treated in a compact wash water treatment scheme, producing a water quality which may be reused in the main production process and a residual concentrated sludge flow.
Wash Water
Water
Reuse
Most water treatment processes are producing waste water, which typically requires further treatment prior to discharge. Therefore options to treat this waste water with the aim to reuse often makes sense.
Cost
Effective
By reducing the wash water volumes and reducing the waste stream the overall water treatment process becomes more cost effective. Various techniques are available to implement a wash water treatment process effectively.
Sustainable solutions
Approach
All water treatment plants produce wastewater. Sand filter backwash water is the largest wastewater component generated. Typically wash water contributes to one to ten percent of total drinking water production. Hence it is obvious to focus upon wash water reuse schemes. Implementing reuse schemes will simultaneously reduce net water intake.
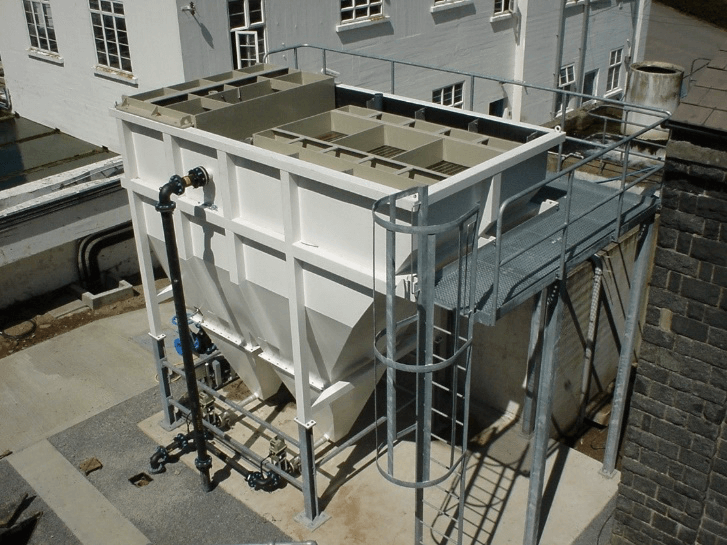
Both discontinuous and continuous wash water reuse schemes are used in practice. The most optimal configuration depends on the actual release of wash water and the wash water storage facilities. Lamella clarifiers, using integrated coagulation and flocculation, showed to be reliable for backwash water treatment. Supplied as standard units, they are equipped with integrated hydraulic mixing and flocculation equipment, including sludge hoppers for simultaneous sludge thickening.
Features
Reliable and compact secondary treatment
A compact wash water treatment process typically consists of coagulation/flocculation, lamella settling and media filtration. Most often a disinfection stage is implemented to avoid cross contamination of the primary treatment process.
Cost effective
Wash water reuse is cost effective as the water to be treated already passed the primary water treatment process. Implementing a secondary wash water treatment process prevents this water to be discharged. It adds up to the net drinking/process water production.
Testimonials
We are happy to collaborate with our clients to meet their objectives. And we highly appreciate their feedback!
If I have to describe Brightwork in three words, I would characterize their capabilities by: reliable, innovative and service driven. I would certainly recommend others to work with them.
Jan Boonstra
Plant operator Wetterskip Fryslân WwTW Franeker
My impression of Brightwork is good, they are very skilful and knowledgeable.
Mattias Feldthusen
Director Process & Product Development
Nordic Water Products AB

Would you like some further reading?
Please feel free to download this whitepaper ‘’ Dealing with backwash water”.









