Phosphorus (P) in waste water discharge into a water body is often the limiting nutrient for primary productivity in the water. Hence excessive P may lead to eutrophication.
There has been an increasing demand to achieve very low effluent total phosphorus due to more stringent discharge limits imposed on waste water treatment plants in Europe. Total P levels below 0.10 mg/l require treatment alternatives, well beyond the current technologies.
What phosphorus fractionation is present in waste water effluent?
Secondary effluent of a well performing plant typically contains total phosphorus levels in the range of 0.4 – 1.2. Actual performance depends on the primary and secondary treatment technologies applied. Total phosphorus is a sum parameter, which should be differentiated to analyse the best possible removal method. Phosphorus is present in soluble (pass 0.45 micron filter) and particulate form. Both soluble and particulate phosphorus consist of reactive P (also indicated as ortho P), poly P and organic P. Dissolved organic phosphorus is hard to remove at all and may contribute to 0.05 – 0.2 mg/l. Always be aware of this! You could reach a threshold which is difficult to pass.
What should the additional treatment look like?
If you want to remove phosphorus to say 0.10 mg/l you need to find ways to remove both particulate and soluble phosphorus effectively. Waste water treatment effluent will – per definition – contain both particulate and soluble phosphorus. Samples at Dutch waste water treatment plants show levels of particulate and soluble phosphorus, both in the range of 0.2 – 0.6 mg/l.
Hence the appropriate tertiary treatment technologies should be able to chemically convert the soluble phosphorus and also be an extremely effective barrier for particulate phosphorus by removing solids.

What should the additional treatment look like?
We have applied three technologies, which have the power to remove phosphorus to levels less than 0.10 mg/l. Disc and cloth filtration are useful as a compact solution which sometimes might fit nicely into the hydraulic line diagram of the existing treatment plant. Continuous media filtration has also proved to be a very suitable solution for phosphorus removal. It also offers the possibility to combine nitrogen and phosphorus removal in one treatment process. We will always seek for the best possible solution for your case.
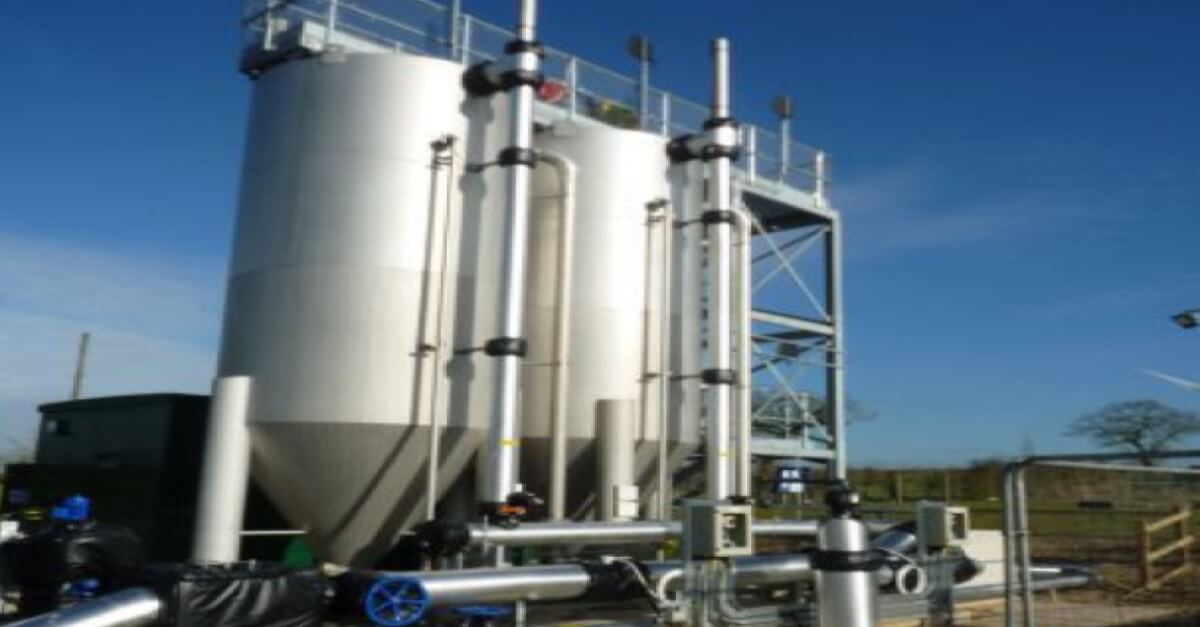
Effluent Reuse Theme Park Efteling
The popular theme park Efteling in the south of the Netherlands launched a drought prevention program. In order to reduce the total volume of ground water abstraction to feed the numerous water ponds in the park. Groundwater levels tended to drop as a result of the abstraction. Therefore effluent from waste water treatment plant Kaatsheuvel is used for replenishing water in the ponds. With particular focus to remove phosphorus to levels below 0.10 mg/l total phosphorus to prevent any eutrophication and algae blooming in the ponds.

Download this paper to find out:
How we manage to consistently meet very low total phosphorus levels with continuous tertiary sand filtration.
How the Sand-Cycle monitoring tool continuously contributes to run the plant without any anomalies.
Which results are obtained year-on-year for various parameters, including total phosphorus, suspended solids, BOD, nitrogen.